standard Twin-Screw Extruder
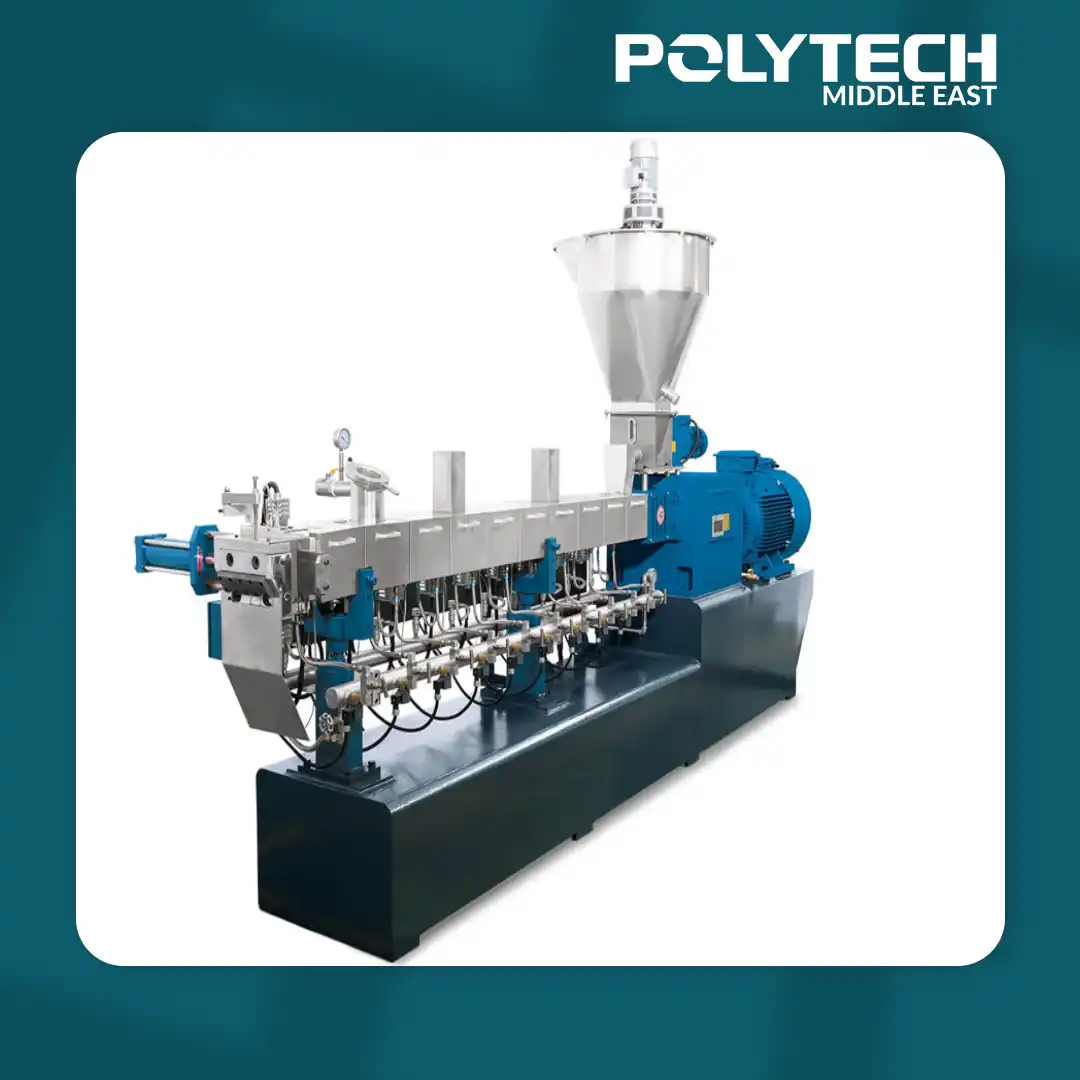

standard Twin-Screw Extruder
Discover our standard twin-screw extruder for plastic production, designed for efficient mixing and consistent, high-quality output. This versatile machine boosts processing speed and productivity in plastic manufacturing.
Description
Introduction to Twin-Screw Extrusion in Plastic Processing
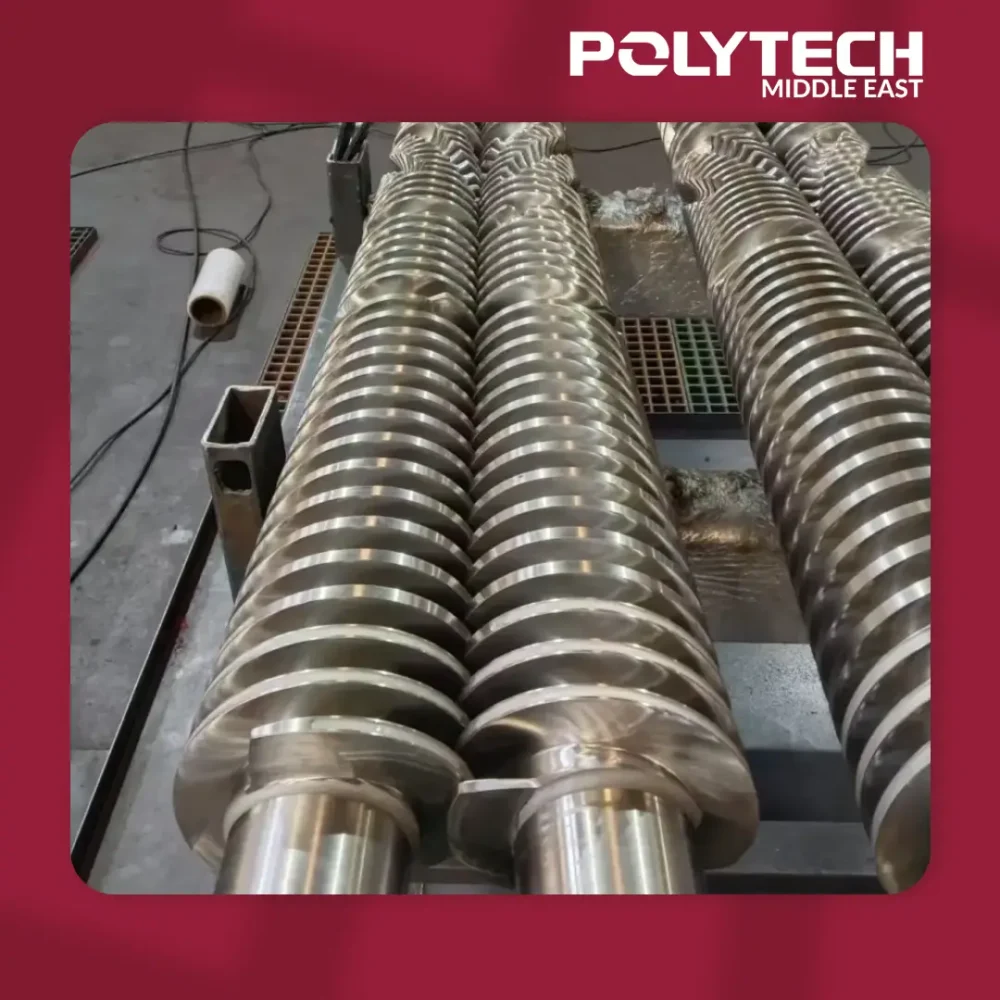
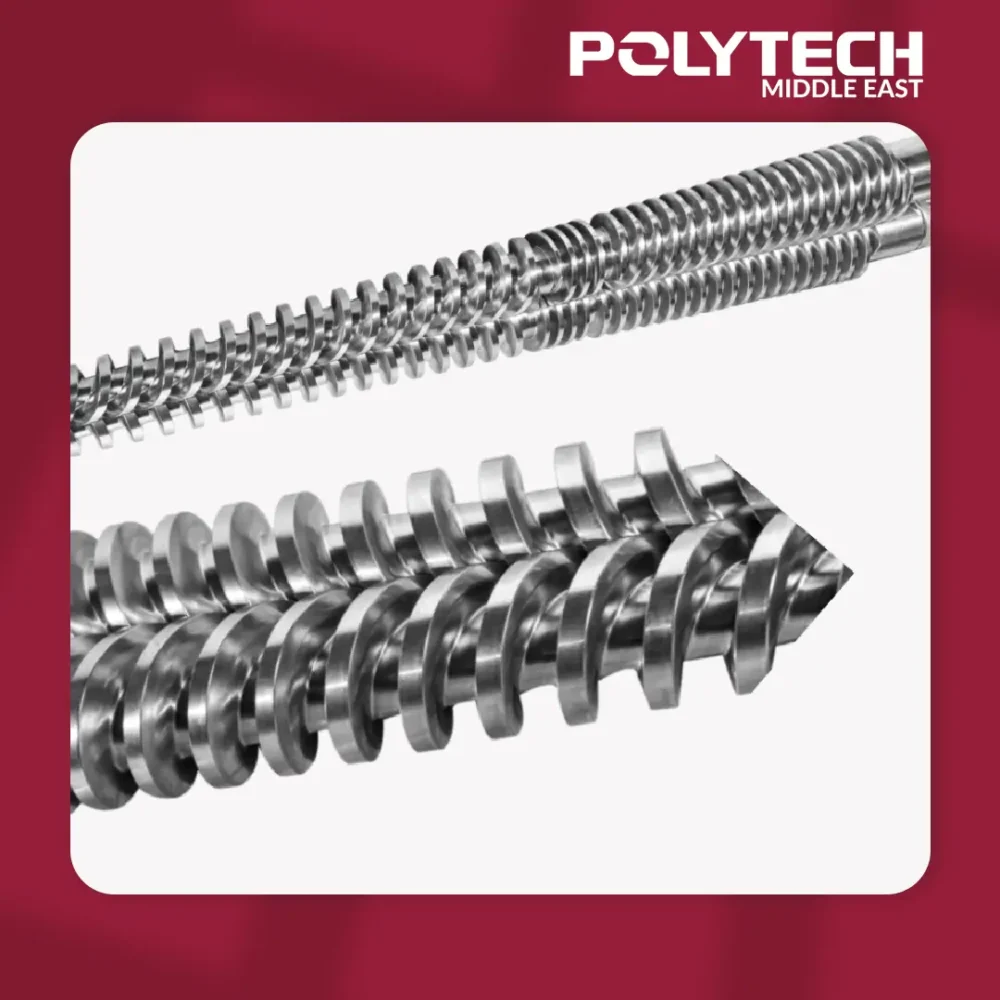
A standard twin-screw extruder is a key machine in modern plastic production. It uses two intermeshing screws inside a heated barrel to efficiently melt, knead, and homogenize polymer materials. This process allows for precise mixing of raw plastic resins and additives, ensuring consistent, high-quality output. Twin-screw extrusion is widely used for producing polymer compounds, color masterbatches, and recycled plastic pellets. In plastic manufacturing, a twin-screw extruder for plastic production serves as a workhorse, providing versatile and reliable processing.
Basic Working Principle of a Standard Twin-Screw Extruder
In a twin-screw extruder, raw plastic pellets and additives are fed through a hopper into a heated barrel with two parallel screws. As the co-rotating screws turn, they intermesh closely, conveying material forward while applying shear and compression. Heat from external elements melts the plastic, and kneading blocks along the screws mix the material thoroughly. The continuous rotation pushes the molten polymer through a shaping die at the end. In this way, the twin screws combine transportation and intense mixing in one step, resulting in a uniform plastic melt ready for shaping.
Key Benefits of Using a Twin-Screw Extruder for Plastic Production
- Superior Mixing and Uniform Quality: Twin-screw extruders excel at dispersing additives and fillers evenly throughout the plastic. Their intense, intermeshing screws deliver outstanding mixing and consistent material dispersion, resulting in uniform product quality across batches.
- High Throughput and Efficiency: Designed for continuous operation, these machines can process plastic at high rates (up to several thousand kilograms per hour). Continuous extrusion reduces downtime between batches, and modern drive systems allow energy-efficient production, lowering operational costs.
- Flexibility and Modularity: Modern twin-screw systems are highly adaptable. Screw elements can be arranged for gentle conveying or aggressive kneading, and sections can be added or changed to suit different materials. Multiple feed ports and venting options let manufacturers add colorants, fillers, or volatile ingredients at precise points. This modular design means one extruder can handle a wide range of plastics and formulations.
- Wide Material Compatibility: These extruders can process a broad variety of plastics (thermoplastics, filled polymers, bio-based resins, etc.). The precise control of temperature and shear makes them suitable for heat-sensitive or reinforced compounds as well.
Investment Advantages: Why a Twin-Screw Extruder is a Good Investment
Investing in a standard twin-screw extruder offers significant long-term value. These machines deliver high throughput and consistent quality, maximizing production efficiency. Their flexible design means one extruder can handle multiple products and formulations, reducing the need for additional equipment. Modern twin-screw extruders are engineered for energy efficiency and ease of maintenance. Features like quick-access barrels allow fast cleaning and reduced downtime. With robust construction and modular components, they ensure reliable performance and a strong return on investment for any plastic manufacturing operation.
Products
Common Applications in the Plastics Industry
Twin-screw extruders are essential in many plastic manufacturing processes:
- Polymer Compounding and Masterbatches: Combining base polymers with additives (colorants, stabilizers, flame retardants, etc.) to create customized plastic compounds.
- Plastics Recycling: Reprocessing waste plastic (regrind or flakes) by melting and reforming it into new pellets or blends.
- PVC and WPC Production: Mixing polyvinyl chloride (PVC) or wood-plastic composites (WPC) with fillers and stabilizers for products like pipes, profiles, and decking.
- Specialty Materials: Processing engineering plastics, biodegradable polymers, and other high-performance materials that require precise compounding.
Applications
Gallery
Main Features
Technical Features (L:D Ratio, RPM, Power, Output)
Standard twin-screw extruders have several key specifications:
- Length-to-Diameter (L:D) Ratio: Typically between 32:1 and 68:1, providing a long processing channel for thorough melting and mixing.
- Screw Speed (RPM): Common operating speeds range from a few hundred up to about 600 rpm, adjustable to balance output rate and heat generation.
- Power: Motor ratings vary widely by model and size, often from tens to several hundreds of kilowatts, driving high torque through the screws.
- Production Capacity: Depending on the machine diameter and speed, throughput can range from a few tens of kg per hour to several thousand kg/hr.
The table below shows typical ranges for a standard twin-screw extruder:
| Type | L:D Ratio | RPM | Power (kW) | Production (kg/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 15–18.5 | 20–80 |
| 40 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 30–37 | 50–120 |
| 50 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 45–55 | 80–200 |
| 52 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 55–75 | 100–250 |
| 60 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 75–90 | 250–400 |
| 65 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 90–110 | 300–550 |
| 75 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 132–160 | 450–750 |
| 85 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 185–250 | 600–1000 |
| 95 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 280–355 | 1200–2000 |
| 110 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 355–550 | 1500–2500 |
| 125 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 450–600 | 1300–2800 |
| 135 | 32:1–68:1 | 400–600 | 630–800 | 3200–7500 |
Related products
-
Machines and Spare Parts
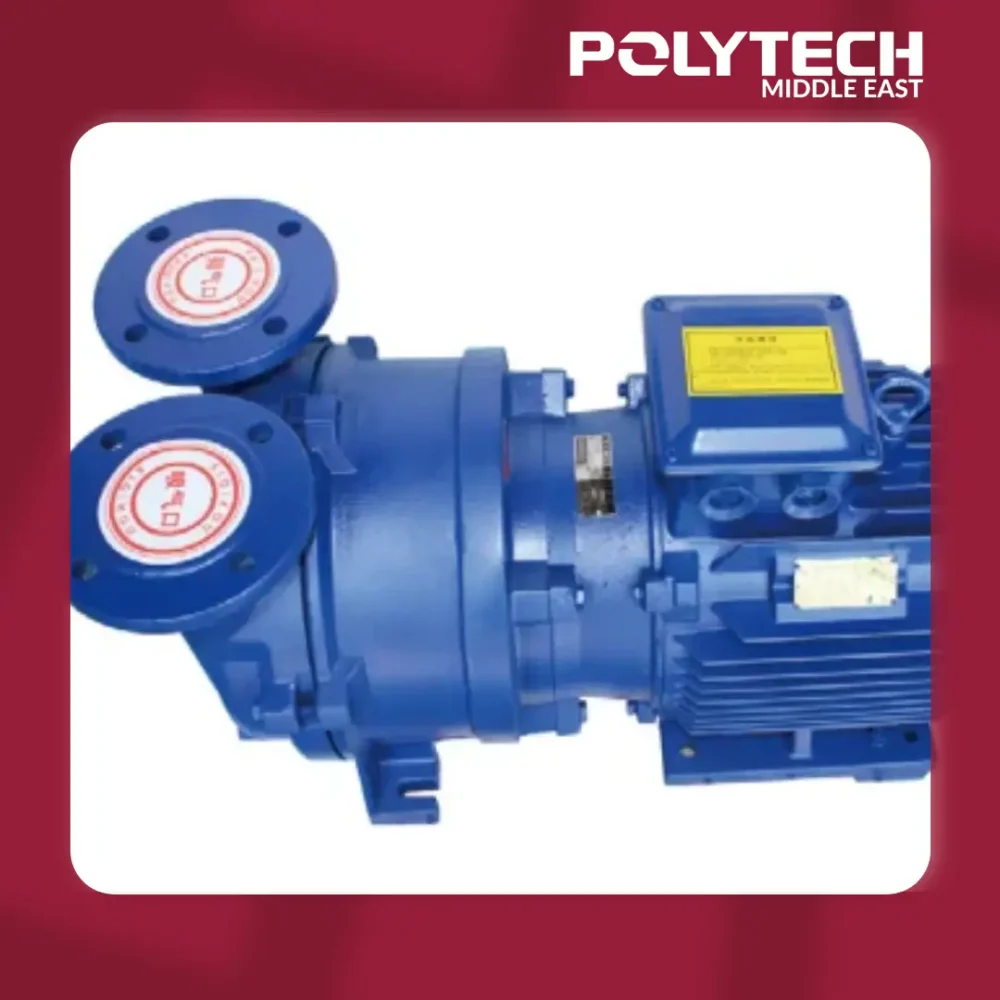
5.5 kW Vacuum Pump
-
Machines and Spare Parts
92/188 Conical Twin-Screw Barrel
-
Machines and Spare Parts
Screws and Barrels for Extrusion
-
Machines and Spare Parts
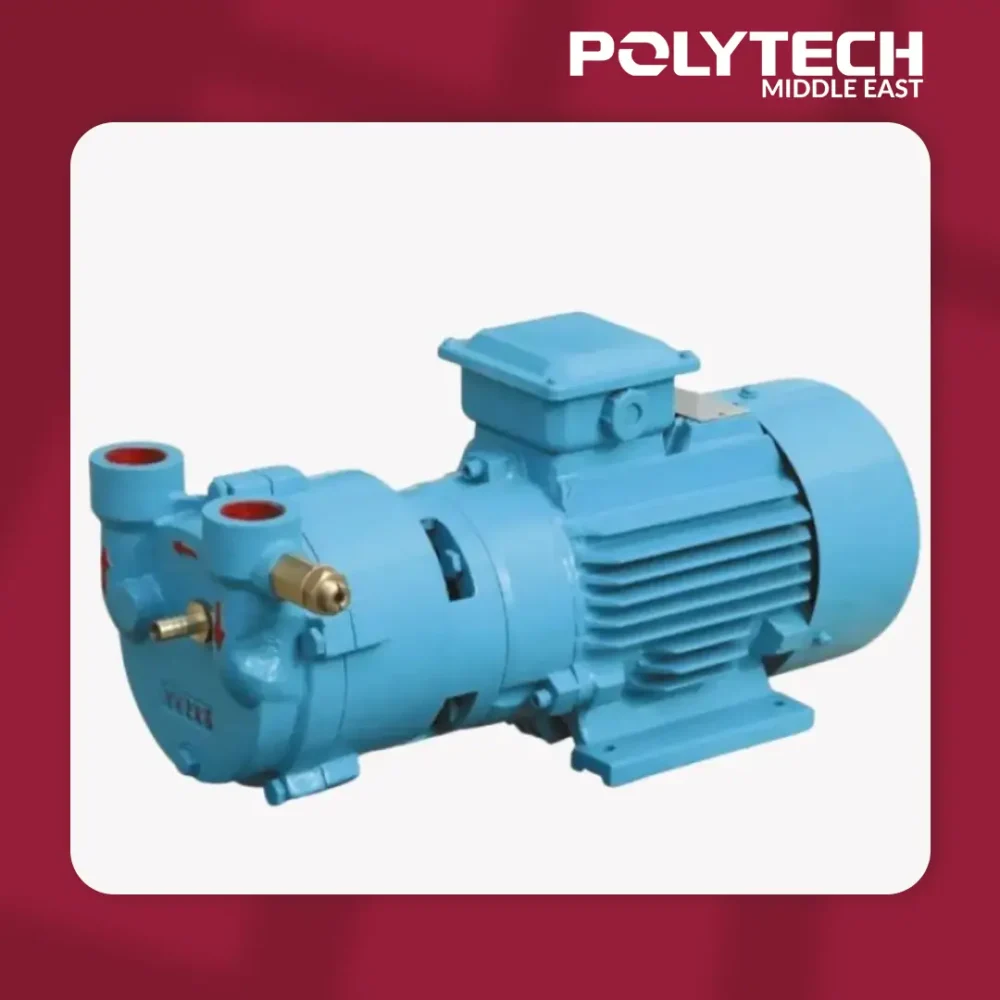
2.2kw Vacuum Pumps for Plastic Extrusion Line