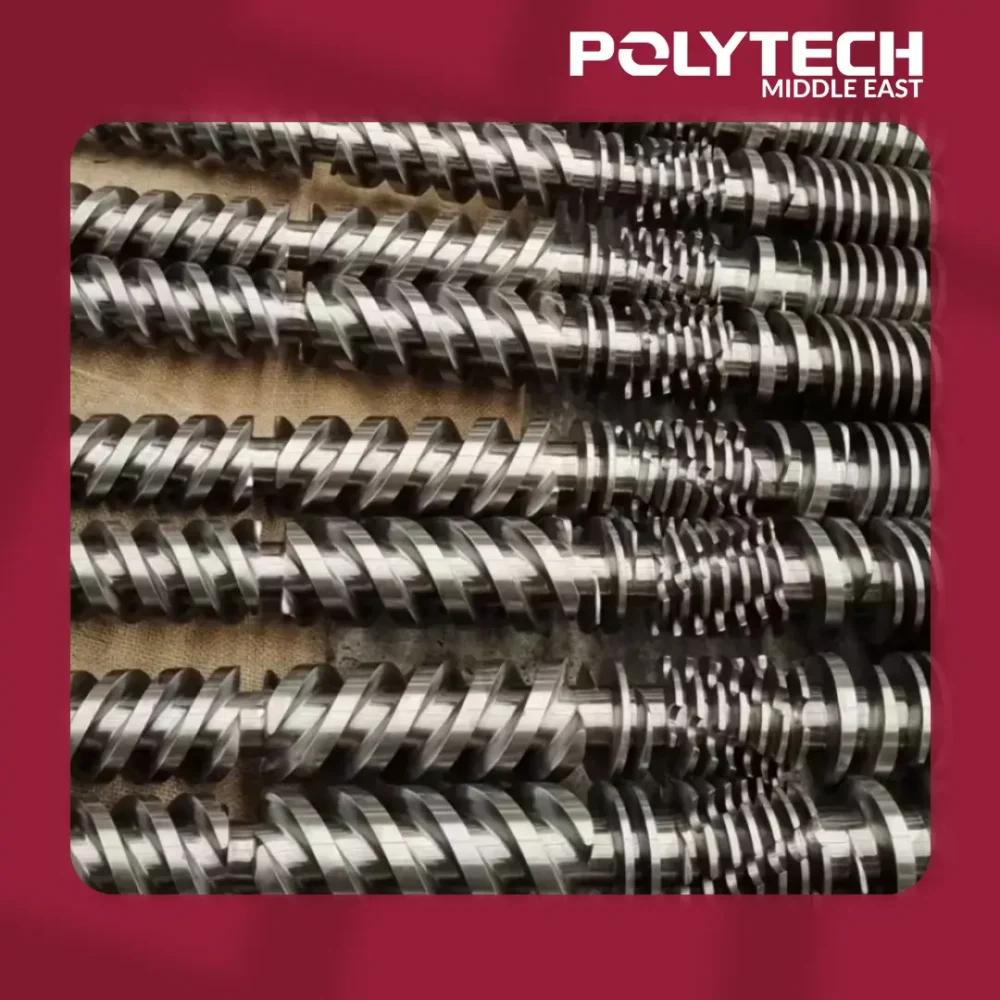
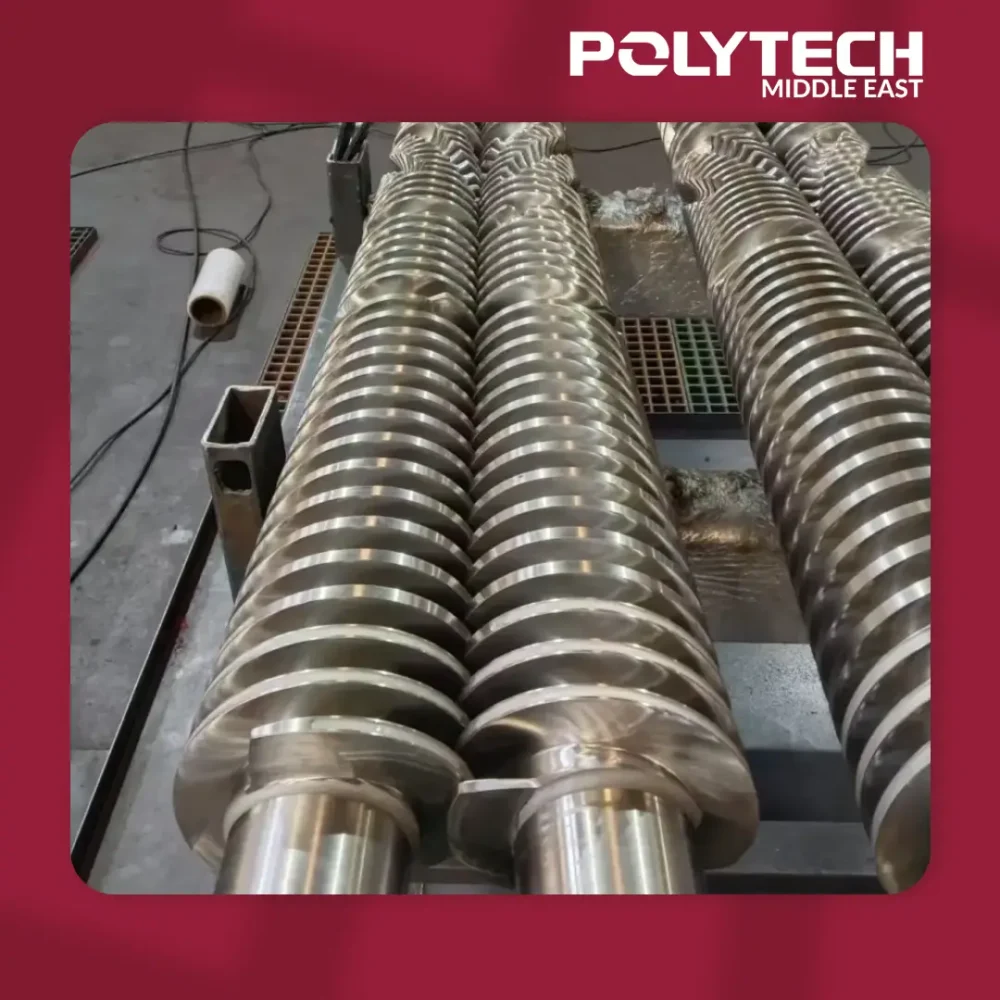
Screws and Barrels for Extrusion
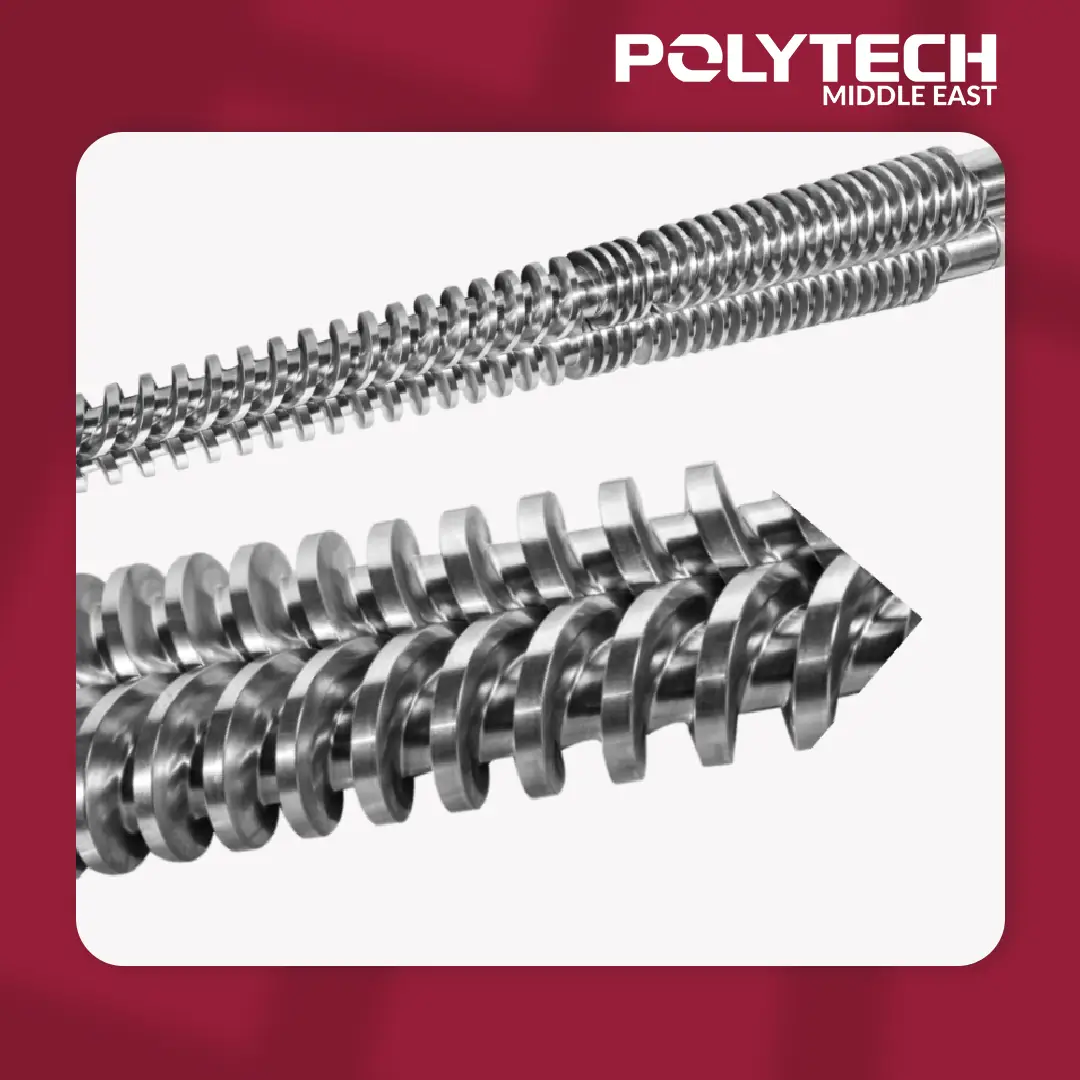
Screws and Barrels for Extrusion
Providing you series of conical twin screw barrels for SPC Sheet with advantages such as long lasting service life, high output and better mixing and improved homogeneity.
Description
Screws and Barrels for Extrusion are two critical components of plastic extrusion machines, playing a fundamental role in the production of high-quality plastic products. These components work together to melt, mix, and push plastic materials through a die to form a continuous shape, which is later cut or processed into the desired product.
The Screw
The screw is a rotating component housed inside the barrel. Its primary function is to transport, compress, and melt the plastic material as it moves along the barrel. The design of the screw directly impacts the efficiency and quality of the extrusion process.
Key Features of the Screw:
- Design:
- Screws have varying designs tailored to specific materials and applications.
- Common designs include single-flight, twin-flight, and mixing screws.
- Zones:
- Screws are divided into three zones:
- Feed Zone: Where the raw material enters and is preheated.
- Compression Zone: Where the plastic melts under heat and pressure.
- Metering Zone: Where the molten plastic is homogenized and prepared for extrusion.
- Screws are divided into three zones:
- Material:
- Screws are typically made of hardened steel or coated with wear-resistant materials to withstand abrasion and high temperatures.
The Barrel
The barrel is the stationary component that houses the screw. It provides the environment where the plastic material is heated and pressurized before being extruded through the die.
Key Features of the Barrel:
- Material:
- Barrels are made from high-strength, heat-resistant materials to endure the extreme conditions of the extrusion process.
- Heating System:
- Equipped with external heaters and temperature sensors to maintain consistent processing conditions.
- Compatibility:
- Barrels are custom-designed to match the screw and the specific requirements of the extrusion process.
How Screws and Barrels Work Together
- As the screw rotates inside the barrel, it pushes the raw plastic material forward.
- The friction between the screw, barrel, and material generates heat, melting the plastic.
- The combination of screw design and barrel temperature control ensures uniform melting and mixing, leading to consistent product quality.
Importance of Screws and Barrels in Extrusion
- Efficiency: Properly designed screws and barrels enhance productivity by optimizing material flow and reducing energy consumption.
- Product Quality: They ensure uniform melting and mixing, reducing defects in the final product.
- Durability: High-quality components minimize wear and maintenance, extending the lifespan of the extrusion machine.
Understanding the role of screws and barrels in plastic extrusion is essential for selecting the right components and achieving optimal results in production. With advancements in material science and engineering, modern screws and barrels offer improved efficiency, durability, and versatility to meet the demands of diverse industries.
Key Features of High-Performance Screws and Barrels
High-Performance Screws
- Optimized Design:
- Incorporates advanced geometries for specific materials to improve mixing and melting.
- Includes features like venting and multi-flight sections for enhanced efficiency.
- Enhanced Wear Resistance:
- Made from high-grade alloys or treated with surface coatings such as nitriding or tungsten carbide to resist abrasion.
- Improved Heat Transfer:
- Designed to ensure consistent heat distribution for uniform melting.
High-Performance Barrels
- High-Temperature Tolerance:
- Constructed using robust materials like bimetallic liners for extended lifespan in high-heat applications.
- Advanced Heating Elements:
- Equipped with efficient heating systems for precise temperature control.
- Customizable Options:
- Tailored to accommodate different screw designs and extrusion requirements.
Importance of High-Performance Features
- Increased Productivity: Enhanced designs reduce cycle times and boost throughput.
- Reduced Maintenance: Durable materials and coatings extend the lifespan, minimizing downtime.
- Superior Product Quality: Uniform mixing and melting ensure consistent end-product properties.
Importance of Screws and Barrels in Extrusion
- Efficiency: Properly designed screws and barrels enhance productivity by optimizing material flow and reducing energy consumption.
- Product Quality: They ensure uniform melting and mixing, reducing defects in the final product.
- Durability: High-quality components minimize wear and maintenance, extending the lifespan of the extrusion machine.
Applications of Screws and Barrels in Plastic Extrusion Machinery
Screws and barrels are indispensable in a variety of plastic extrusion applications, each tailored to meet specific production requirements. Below are some of the most common uses:
Film and Sheet Extrusion
- Produces thin plastic films used in packaging, agriculture, and industrial applications.
- Specialized screws and barrels ensure uniform thickness and high transparency.
Pipe and Profile Extrusion
- Manufactures pipes for water supply, sewage systems, and electrical conduits, as well as custom profiles for construction and automotive industries.
- Components are designed to handle high pressure and maintain dimensional accuracy.
Blown Film Extrusion
- Produces flexible plastic films used for bags, stretch wrap, and shrink wrap.
- Screws are optimized for precise control of bubble stability and film thickness.
Extrusion Coating
- Applies a thin layer of plastic onto substrates like paper, foil, or textiles.
- Screws and barrels ensure even coating and adhesion quality.
Wire and Cable Coating
- Extrudes insulating and protective layers around electrical wires and cables.
- High-performance components maintain consistent coating thickness and dielectric properties.
Recycling and Compounding
- Reprocesses plastic waste into usable raw material or blends additives with polymers for enhanced properties.
- Durable screws and barrels withstand abrasive materials and high processing temperatures.
Injection Molding Pre-Processing
- Prepares plastic granules for subsequent injection molding operations.
- Ensures uniform melt consistency and proper pellet sizing.
Choosing the Right Extruder Screws and Barrels Solutions
1. Material Compatibility
- Identify the type of plastic material you are processing (e.g., polyethylene, PVC, polypropylene).
- Choose screws and barrels designed to handle the material’s specific melting point and viscosity.
2. Application Requirements
- Consider the end product’s specifications, such as thickness, transparency, or strength.
- Ensure the selected components align with the production process, whether for film, pipes, or recycling.
3. Screw and Barrel Design
- Opt for specialized designs like mixing screws for blending additives or vented screws for degassing.
- Match the barrel’s internal dimensions to the screw for optimal performance.
4. Wear Resistance
- Select components with wear-resistant materials or coatings to withstand abrasive and corrosive materials.
- Features like bimetallic linings or tungsten carbide coatings extend longevity.
5. Heating and Cooling Efficiency
- Ensure the barrel is equipped with precise heating elements and cooling systems.
- Efficient temperature control prevents material degradation and ensures consistent output.
Types of Screws for Extrusion Machines
Parallel, single, and conical twin screws are common designs used in plastic extrusion machines. Each type serves specific purposes and offers unique advantages depending on the application requirements.
Parallel Screws
- Description: Two screws rotate in parallel alignment, either co-rotating or counter-rotating.
- Applications:
- Ideal for mixing and blending applications.
- Commonly used in twin-screw extruders for compounding and producing filled plastics.
- Advantages:
- Excellent mixing capabilities.
- Handles high output with consistent quality.
- Suitable for heat-sensitive materials.
Single Screws
- Description: A single helical screw operates within a barrel to melt and push plastic material forward.
- Applications:
- Widely used for general-purpose extrusion, such as film and pipe production.
- Suitable for materials with stable melting properties.
- Advantages:
- Simpler design and lower cost.
- Easier maintenance compared to twin screws.
- Efficient for standard processing needs.
Conical Twin Screws
- Description: Two screws positioned at an angle, converging towards the die end of the extruder.
- Applications:
- Ideal for processing PVC and other thermoplastics with high viscosity.
- Commonly used in pipe and profile extrusion for large-diameter products.
- Advantages:
- High compression and mixing efficiency.
- Excellent material feeding and melting performance.
- Compact design, suitable for space-limited setups.
Materials Used in High-Performance Screws and Barrels
The materials used in manufacturing screws and barrels are critical for their performance, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. Below are the most common materials employed in high-performance applications:
1. Hardened Steel
- Applications: Used for both screws and barrels requiring high strength and resistance to deformation under pressure.
- Advantages:
- Excellent durability and wear resistance.
- Handles high-temperature operations effectively.
2. Bimetallic Alloys
- Applications: Commonly used for barrels in extrusion processes involving abrasive materials.
- Advantages:
- Superior abrasion and corrosion resistance.
- Longer lifespan compared to single-material options.
3. Nitrided Steel
- Applications: Suitable for screws exposed to moderate wear and corrosion.
- Advantages:
- Improved surface hardness.
- Cost-effective for standard applications.
4. Tungsten Carbide Coatings
- Applications: Ideal for screws and barrels processing highly abrasive or filled plastics.
- Advantages:
- Exceptional hardness and wear resistance.
- Prolongs the service life of components.
5. Stainless Steel
- Applications: Used in corrosive environments or for processing materials sensitive to contamination.
- Advantages:
- High resistance to rust and chemical damage.
- Ensures cleanliness in the extrusion process.
6. Chrome Plating
- Applications: A surface treatment applied to enhance the durability of screws and barrels.
- Advantages:
- Reduces friction and wear.
- Provides a smooth surface for consistent material flow.
Maintenance Tips for Screws and Barrels
Regular maintenance of screws and barrels is essential to ensure optimal performance, prolong their lifespan, and prevent costly downtime. Below are some key maintenance tips:
1. Routine Cleaning
Why: Prevents material buildup, which can cause defects in the final product.
How:
- Use appropriate cleaning compounds or purge materials.
- Clean the screw and barrel after processing different materials or during extended downtime.
2. Monitor Wear and Tear
Why: Detects early signs of damage, such as scratches, corrosion, or reduced performance.
How:
- Perform regular visual inspections.
- Measure the screw diameter and barrel thickness to identify wear.
3. Use Proper Operating Conditions
Why: Avoids unnecessary stress on components.
How:
- Maintain recommended processing temperatures and pressures.
- Avoid sudden changes in operating conditions.
4. Lubrication
Why: Reduces friction and prevents overheating.
How:
- Apply the correct type and amount of lubricant as specified by the manufacturer.
- Ensure lubrication systems are functioning properly.
5. Replace Worn Components
- Why: Ensures consistent product quality and prevents further damage.
How:
- Replace worn screws, barrels, or liners promptly.
- Use original or high-quality replacement parts.
6. Avoid Processing Contaminated Materials
- Why: Prevents abrasive damage and corrosion.
How:
- Use clean, high-quality raw materials.
- Screen materials to remove foreign objects.
7. Store Components Properly
- Why: Protects components during downtime or storage.
How:
- Store screws and barrels in a dry, clean environment.
- Cover components to protect them from dust and moisture.
8. Maintain Heating and Cooling Systems
- Why: Ensures consistent temperature control for efficient operation.
How:
- Regularly check and calibrate heaters and sensors.
- Inspect cooling systems for blockages or leaks.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance
- Improved Efficiency: Maintains consistent production rates and quality.
- Extended Lifespan: Reduces wear and delays the need for replacements.
- Cost Savings: Prevents unplanned downtime and expensive repairs.
Products
Applications
Gallery
Main Features
Product Material
| Raw Material | The Finished Product Processing Requirements |
|---|---|
| 38CrMoAlA, SACM645, 42CrMo | Nitriding Treatment |
| 42CrMo, AISI 4140 | Chrome Plating Hardness Layer |
| 4Cr5MoSiV1, SKD-61, SKD-11 | Spraying Bimetal Alloy Layer and Nitriding Treatment |
| HPM38, SI36, SUS440, 9Cr18MoV | Stainless Steel(Iron), High Frequency Quenching |
| GHII3 | Nature Harden After High Temperature |
Related products
-
Machines and Spare Parts
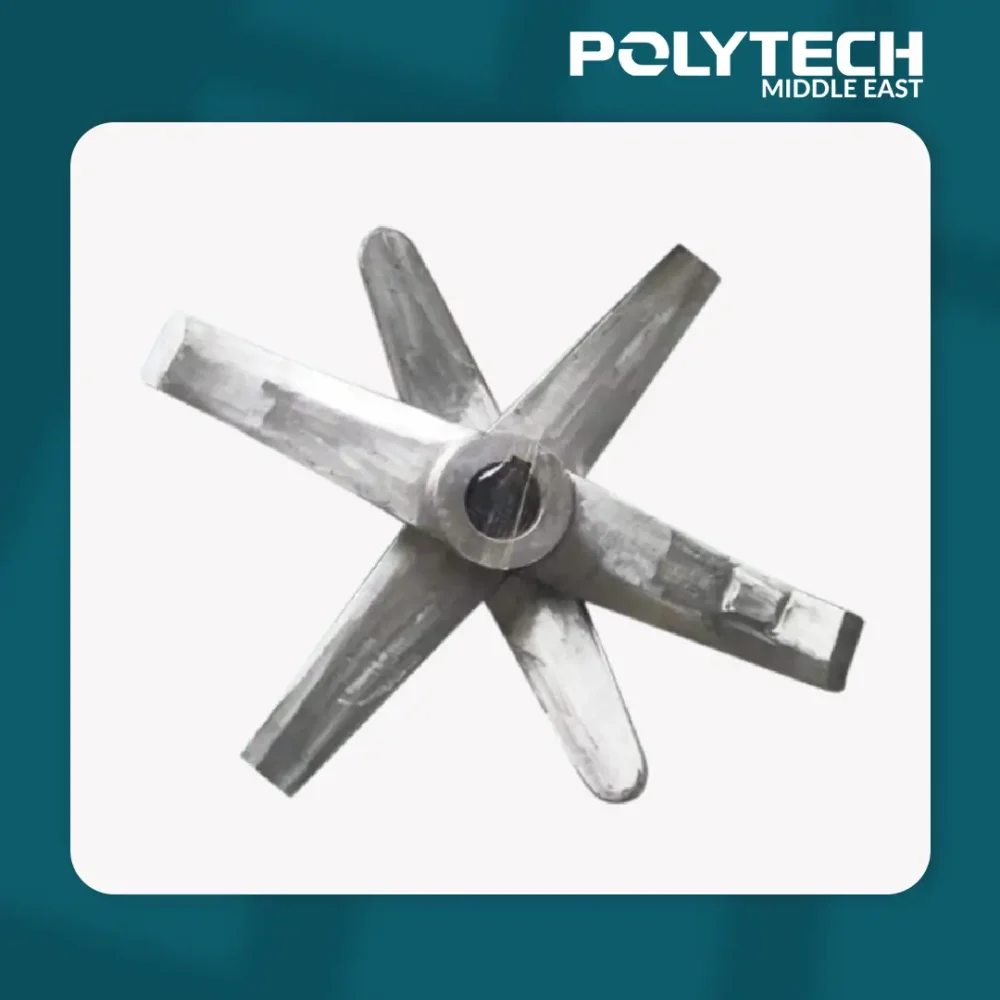
PVC Mixer Blades
-
Machines and Spare Parts
51/105 Conical Twin Screw Barrel
-
Machines and Spare Parts
92/188 Conical Twin-Screw Barrel
-
Machines and Spare Parts
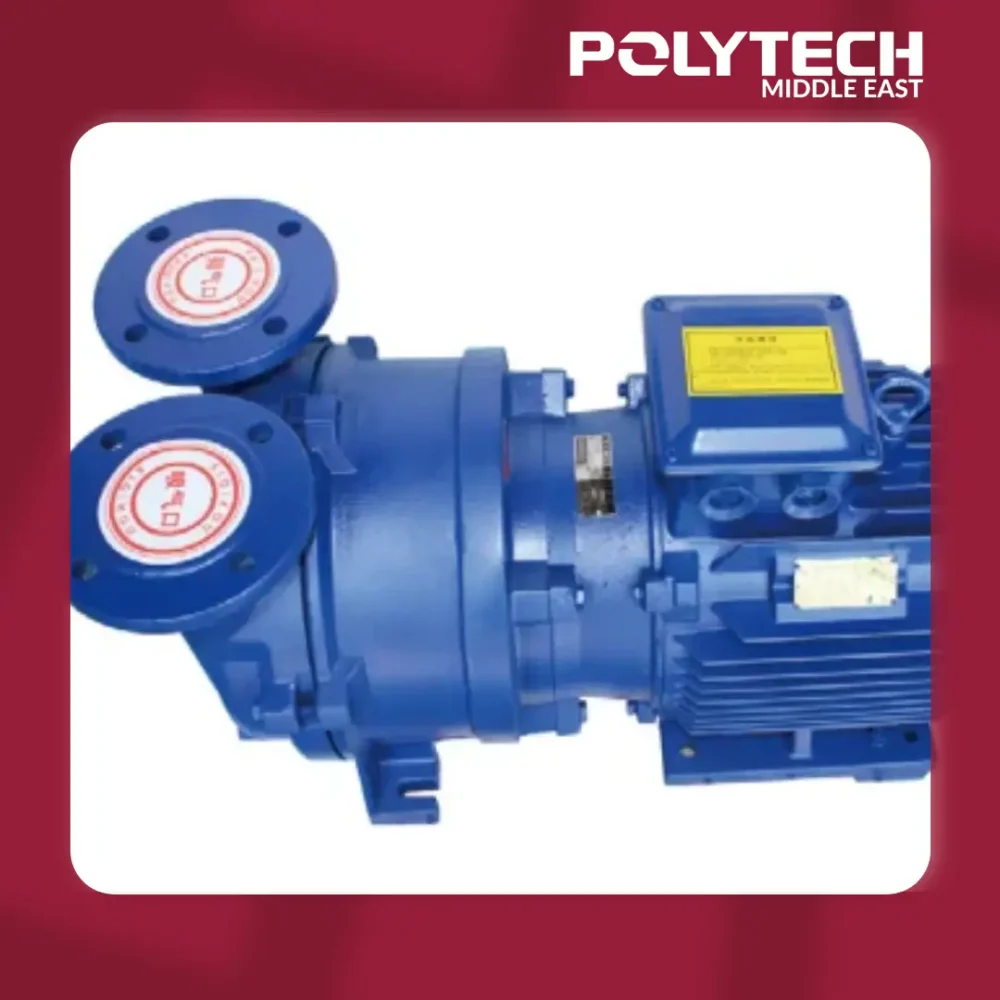
5.5 kW Vacuum Pump